General Market Environment
Global economy1
The global economy expanded at a rate of 3.2 percent in 2024, according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Economic momentum thereby continues to stand below the level of the pre-Covid period, when the average for the years 2000 to 2019 amounted to 3.7 percent. The US economy performed well with growth of 2.8 percent, mainly thanks to strong domestic demand. In some European countries, by contrast, recession continued, with growth in the overall Eurozone amounting to 0.8 percent. The continued high level of energy prices due to the Russian war of aggression against Ukraine, the tightening of monetary policy in previous years, and persistently high levels of inflation exerted a dampening effect. Although consumer confidence recovered slightly compared to the previous year, it remained at a low level in absolute terms. At 4.8 percent, Chinese economic growth also fell short of both expectations and the government’s target. While export demand recovered, growth was slowed by weak domestic consumption and the ongoing crisis in the real estate market. The IMF forecasts growth of 3.3 percent for 2025.
Although demand along the value chain in the textile and apparel industry improved slightly year-on-year, this was at least partly due to accelerated purchasing effects in anticipation of higher trade barriers, particularly towards the year-end. Prices remained under pressure. Satisfaction with the business situation rose over the course of 2024, according to a global survey conducted by the International Textile Manufacturers Federation (ITMF).2 Most market participants, however, continue to view the situation negatively.
Global fiber market3
Continued stable growth in global fiber production
Global retail apparel sales in 2024 (after adjusting for price effects) reported hardly any year-on-year change, according to preliminary estimates. While demand stagnated in China and even decreased in Europe, it proved to be more stable than expected in the USA.
Following a reduction in stock levels in the clothing retail sector over the course of the previous year, stocks were built up again in 2024, which was at least partly due to orders being brought forward in light of the threat of US import tariffs. Meanwhile, stock levels in the upstream production stages barely rose.
Demand for home textiles in 2024 continued to be negatively impacted by reduced levels of construction activities due to high interest rates and investments brought forward during the Covid pandemic.
As in previous years, retail sales of hygiene products in the nonwovens industry proved to be crisis-resistant. Sales volumes of major brands were stable to slightly lower, while demand for lower-priced brands was stronger.
Fibers on the world market
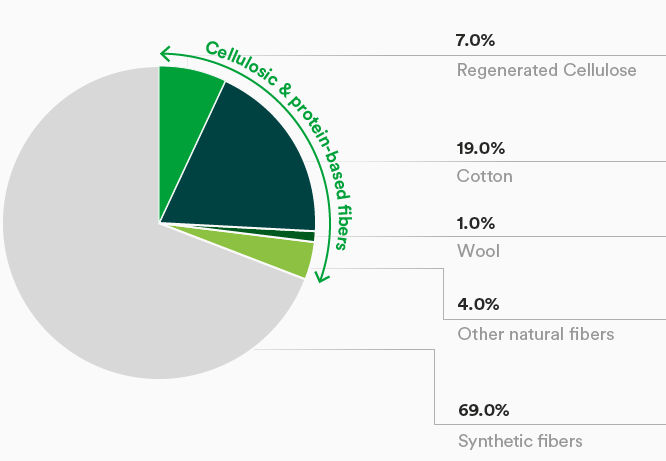
Global fiber production rose by slightly more than 3 percent to 126 mn tonnes in 2024, according to initial estimates. This growth is in line with the long-term average.
The cotton harvest decreased by around 1 percent to 24.1 mn tonnes during the past 2023/2024 season. Cultivated areas were down for the second consecutive year, by just under 2 percent, while the global average yield per hectare rose slightly. Higher production levels in Brazil and Pakistan almost completely offset reduced harvest levels in China, India, and the USA. Brazil replaced the USA as the most important exporter for the first time. Demand for cotton recovered by just under 6 percent to reach a level of 25 mn tonnes. As a consequence, stocks reduced by 5 percent to 18.5 mn tonnes. The production of other natural fibers such as wool, linen, hemp, and silk also decreased by 4 percent year-on-year.
The production of regenerated cellulosic fibers such as lyocell, modal, and viscose fibers rose by 8 percent to 8.4 mn tonnes, according to initial estimates. This growth mainly reflected higher capacity utilization at viscose plants followed by a global increase in lyocell fiber production.
Production volumes of synthetic polymer fibers amounted to around 87.5 mn tonnes, up 5 percent year-on-year, according to initial estimates.
Global fiber production 2024*
by type of fiber in percent (basis = 126 mn tons)
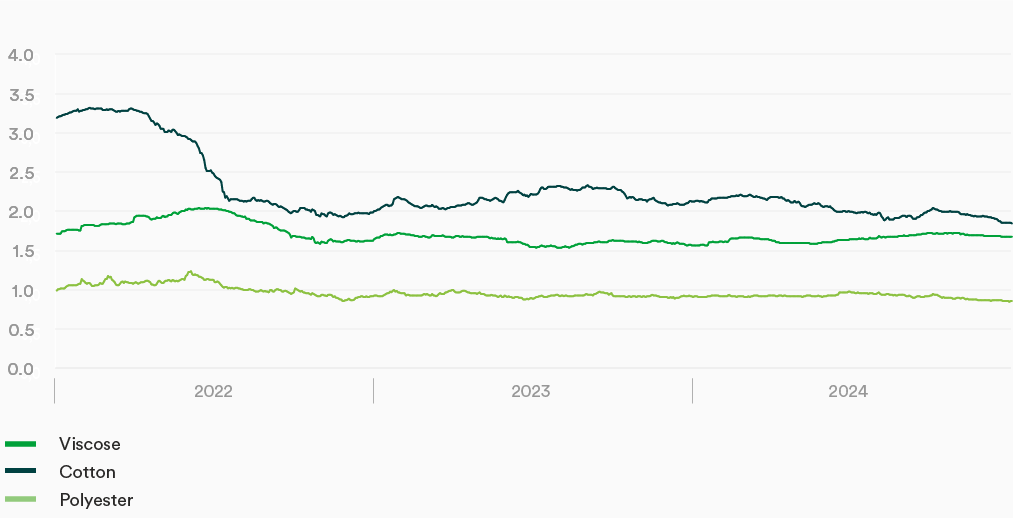
Variation in staple fiber prices
Price trends on staple fiber markets proved to be mixed in 2024. While cotton and polyester prices decreased, viscose prices rose slightly.
However, cotton prices proved to be very volatile. While the Cotlook A index started the year at 91 US cents per pound and rose to as high as 107 US cents per pound in February, it was down 14 percent over the course of the year to 79 US cents per pound following a slight recovery in the fall. This index last fell to below the 80 US cents per pound level in December 2020.
The price of polyester staple fiber in China also decreased over the course of the year. Although it reached a high of RMB 7,940 per tonne in July due to higher costs for crude oil and the intermediate products required for fiber production, it then fell to RMB 6,980 per tonne by the end of the year. Over the year as a whole, this represents a reduction of 5 percent.
Viscose prices in China rose by 9 percent over the course of the year to RMB 13,750 per tonne. However, the average year-on-year increase in 2024 was moderate at just 3 percent. The 2024 year was characterized by high capacity utilization in Chinese viscose plants of in excess of 85 percent and low average annual stock levels of around ten days – both levels were last reached in 2017 and indicate an increasing level of equilibrium between supply and demand. However, the economic situation for manufacturers that lack backward integration remained challenging.
The price premium for differentiated specialty fibers from the TENCEL™, LENZING™ ECOVERO™, and VEOCEL™ brands proved to be comparatively resilient.
With the exception of minimal corrections, the Chinese import price for dissolving wood pulp, the key raw material for regenerated cellulosic fiber production, rose continuously over the course of 2024 and, at USD 970 per tonne at the end of December, stood 10 percent higher than at the start of the year. The average price for the year also rose by 7 percent. This is all the more remarkable given that the Chinese price for hardwood pulp decreased by more than USD 150 per tonne in August and continued to fall until the year-end.
As in the previous year, dissolving wood pulp decoupled from this trend, as limited supply encountered high demand from fiber manufacturers. The price premium for dissolving wood pulp reached an unusually high level of USD 425 per tonne at the end of the year.
Staple fiber prices – Development in China*
USD/kg (excl. VAT)
1 Source: IMF, World Economic Outlook, January 2025
2 Source: ITMF, 30th Global Textile Industry Survey, January 2025
3 All production figures in this section have been updated compared to the initial estimates published in the 2023 Annual Report. Sources: The Fiber Year, ICAC, Cotton Outlook, CCFG, FAO
