Sourcing
[ESRS G1-2; GRI 204-1, 308-1, 308-2, 414-1]
The metrics in this section are not validated by an external body other than the assurance provider.
Directives and polices are implemented in the contact with suppliers. In this regard, Lenzing can act as a role model in business conduct within the industry, while also expecting the same standards from its business partners.
Wood, pulp and chemicals purchasing are handled by three different teams within the Lenzing Group. Lenzing aims to minimize purchasing risks, such as major price fluctuations and supply bottlenecks through reliable, long-term supply relationships and active supplier management.
The most important materials procured are (in order of annual procurement volume): wood, dissolving wood pulp, caustic soda, sulfuric acid, sulfur, carbon disulfide, sulfur dioxide and magnesium oxide.
In 2024, when screening for risk suppliers, no Lenzing suppliers were identified as having significant actual and potential negative environmental impacts.
Sustainable chemical sourcing
The most significant chemicals used in the Lenzing Group – amounting to approximately 85 percent of the overall purchase volume – are caustic soda (NaOH), carbon disulfide (CS2), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), sulfur (S), sulfur dioxide (SO2), softening agents, flame retardants, modifiers, N‑methylmorpholine N‑oxide (NMMO), titanium dioxide (TiO2), and zinc sulfate (ZnSO4). Figures for chemical sourcing are not provided for confidentiality reasons.
The target of assessing 80 percent of the most important chemical suppliers (by purchasing value) was reached in 2019. Additional suppliers continue to be assessed (table “Number of suppliers responding to EcoVadis questionnaire since the introduction of the assessment in 2017”). The supplier base can change in line with the prevailing market environment. Hence, the current “Supplier engagement” target aims to continuously engage with the key suppliers that cover more than 80 percent of budget spend on procurement, in order to improve their sustainability performance. This target has also been extended to include assessment possibilities other than EcoVadis. As a measure under this target, Lenzing has agreements signed with the key chemical suppliers including sustainability clauses. Some of these conditions include setting GHG reduction targets approved by the Science Based Target initiative (SBTi), to provide information on the product carbon footprint and water scarcity at facilities where Lenzing sources products.
Training of Buyers
To align with Lenzing’s commitment to supply chain due diligence and enhance supplier engagement, the global purchasing team undergoes ongoing trainings facilitated by EcoVadis. This training is provided through EcoVadis platform sessions or via internal training sessions using information from the EcoVadis website. Purchasers who participate in these initiatives gain access to the EcoVadis platform, empowering them to deepen their understanding of sustainability through the available EcoVadis academy. Constant support and engagement is provided by a sustainability and supply chain expert at Lenzing, who coordinates and supports sustainability practices that are relevant to buyers.
EcoVadis Score of Lenzing’s suppliers / supplier evaluation
For more information, please see the “Actions” section in the “Workers in the value chain chapter”.
Supplier management
Active negotiations with suppliers regarding their engagement for sustainability assessment are an ongoing process. Currently more than 800 suppliers have been assessed on the basis of social and environmental criteria through the EcoVadis tool.
2024 |
824 |
2023 |
608 |
|---|---|
2022 |
387 |
2021 |
163 |
2020 |
152 |
2019 |
102 |
2018 |
93 |
2017 |
82 |
|
Regionally purchased |
Not regionally purchased |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
2024 |
87% |
13% |
||
2023 |
88% |
12% |
||
2022 |
73% |
27% |
||
2021 |
94% |
6% |
||
|
||||
In 2024, 80 percent of all purchased liquid metric tons of chemicals were delivered by 36 suppliers (compared to 30 suppliers in 2023). Relationships with these suppliers are highly stable in general. In 2022, due to the scarcity of caustic soda in the European market, a higher volume was imported from other regions. The availability of caustic soda continuously stabilized during 2023, which led to a higher proportion of regionally purchased chemicals compared to 2022.
Sustainable wood and dissolving wood pulp sourcing
Wood and dissolving wood pulp are Lenzing’s most important raw materials. The Lenzing Group takes responsibility by focusing on sustainable sourcing covered by certification, responsible consumption, and the highly efficient use of these valuable resources.
Lenzing sources wood and dissolving wood pulp from semi-natural forests (as defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations1, FAO, which include naturally regenerating and planted forests of similar species composition as the natural forests in the area) and plantations, as all defined by FAO2, but not from primary, natural or ancient and endangered forests.
Assuming a dissolving wood pulp yield from wood of 40 percent, a rough estimate for the total yearly wood input of Lenzing’s regenerated cellulose fibers would be 2.5 million tons (dry matter), spread between Lenzing’s own production and the dissolving wood pulp purchased.
In addition to its own dissolving wood pulp production, Lenzing procures dissolving wood pulp in the global market, mostly under long-term supply contracts. On the other hand, a share of its pulp production is traded on the global dissolving pulp market. In 2024, the Lenzing Group procured pulp from the following suppliers (in alphabetical order):
Supplier |
Country |
|---|---|
AustroCel Hallein GmbH |
Austria |
Georgia-Pacific LLC |
USA |
International Paper |
USA |
Lenzing AG |
Austria |
Lenzing Biocel Paskov a.s. |
Czech Republic |
LD Celulose (Lenzing Group) |
Brazil |
Rayonier Advanced Materials |
USA, Canada |
Sappi Ltd. |
South Africa, USA |
Södra Skogsägarna ekonomisk förening |
Sweden |
Re:NewCell AB |
Sweden |
Regional wood supply in Europe
Regional wood supply is important to Lenzing, as this is one measure to reduce GHG emissions stemming from transport. Lenzing is committed to source the wood for its pulp mills in Europe as locally as possible. Lenzing operates three pulp mills in which wood is turned into dissolving wood pulp. The Lenzing site (Austria) mainly uses beech wood plus small amounts of other hardwoods and spruce, whereas the Paskov plant (Czech Republic) mainly uses spruce. The plant in Indianópolis (Brazil) exclusively uses eucalyptus from a plantation under its own operation.
Wood sourcing for the Lenzing Group’s own pulp mills in Lenzing (Austria) and Paskov (Czech Republic)
Beech and spruce by country, 2022–2024.
“Other countries” for Lenzing sites are France, Switzerland, Croatia and Poland.
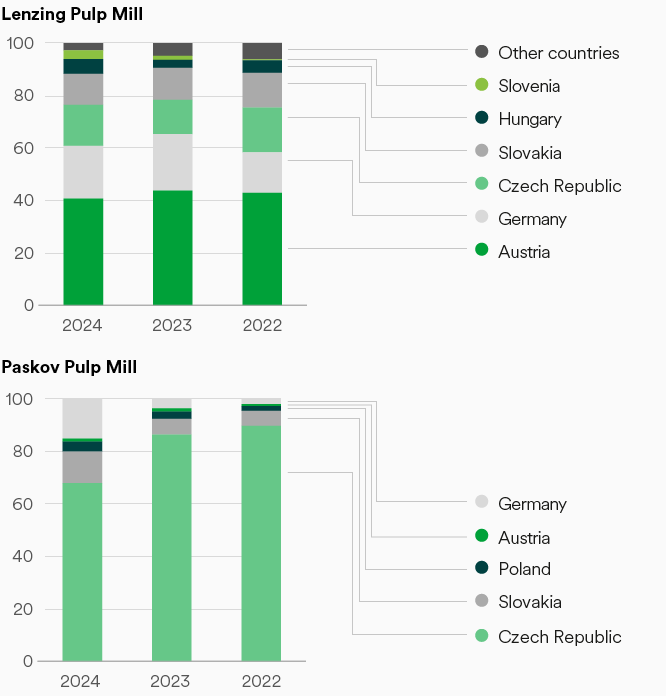
To ensure efficient logistics, the vast majority of the wood required is regionally sourced, minimizing transportation routes and delivery times. For the Lenzing site (Austria) regional3 wood accounted for 93.8 percent in 2022, 96.5 percent in 2023, and 97.1 percent in 2024. For the Paskov site (Czech Republic), the regional supply rate has been constant at 100 percent since 2019. For the underlying figures, please see the Annex.
Local wood supply in Brazil
Lenzing’s pulp mill in Brazil, a joint venture with Dexco under the name of LD Celulose, uses wood from its own plantations. Currently, 93,908 hectares of plantation are managed, including 22,980 hectares (table ”Quantitative description of areas managed and influenced by LD Celulose (entity-specific disclosure)” in the “E4 Biodiversity and ecosystems” chapter) of protected area, which is not used for wood sourcing but to ensure the protection of flora, fauna, and water. These plantations operate completely in accordance with the Lenzing Group’s guidelines and high standards for sourcing wood and pulp, as well as the requirements of the leading certification schemes.
The forest unit responsible for supplying LD Celulose’s wood is located in Triângulo Mineiro in the State of Minas Gerais. The area that was transformed into the LD Celulose plantation unit has been used for cattle raising, intensive agricultural activities and eucalyptus forestry since the 1970s. No native (primary) forest was converted to establish the LD Celulose plantation. The current types of land use within the plantation are described in the section ”Metrics for biodiversity and ecosystem enhancement within LD Celulose’s plantations” of the “E4 Biodiversity and ecosystems” chapter. The plantations are located more than 800 kilometers away from the region that comprises the Amazon rainforest.
Supplier evaluation wood and pulp
All key suppliers of wood and dissolving pulp are evaluated for sustainability. Lenzing conducts regular audits, as well as specific evaluations of both new and established suppliers for sustainability, including compliance with environmental and safety standards. Suppliers are interviewed regularly and evaluated under environmental and safety aspects with the support of external experts. A final assessment is then conducted. This affects the overall supplier assessment and constitutes a major criterion for long-term cooperation with suppliers.
Lenzing’s key suppliers are mostly those that have a certain size and volume. Lenzing is taking a closer look at these, as non-compliance with them represents a greater risk for Lenzing. Pulp suppliers are assessed using a due diligence system based on the FSC® Controlled Wood criteria. This includes the annual assessment of the sustainability performance of pulp suppliers, using a comprehensive questionnaire covering aspects such as procurement standards, supply areas, supply chain traceability, and GHG emissions. The results of the survey are used to identify the key sustainability issues and guide Lenzing’s future supplier engagement activities.
All wood suppliers – totaling more than 600 in 2024, half of which are private owners – in all sourcing countries are assessed once a year against FSC® Controlled Wood and PEFC Controlled Sources criteria. All pulp suppliers are certified by the leading forest certification schemes and supply Lenzing with certified or controlled pulp.
Wood and dissolving wood pulp certifications
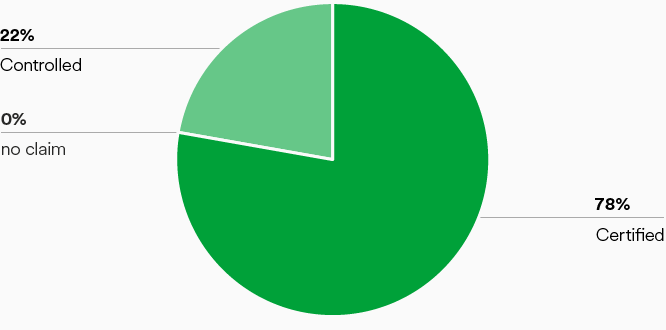
Lenzing’s wood procurement management system ensures that all wood for pulp production is sourced from legal and sustainably managed sources. Lenzing demonstrates that the wood sourcing complies with its high standards through verification based on FSC® and PEFC certification systems (figure “Certification status”). 100 percent of wood and dissolving wood pulp used by the Lenzing Group for fiber production for the market is either certified by FSC® and PEFC or controlled and inspected in line with these standards (figure “Certification status - overall certified and controlled wood”).
The following figures show the certification status of all wood or pulp input into Lenzing’s fiber production, whether obtained directly through its own procurement for in-house dissolving wood pulp mills or indirectly through dissolving wood pulp suppliers. All Lenzing Group production sites are FSC® CoC (Chain of Custody) certified. The multi-site certification for PEFC CoC currently covers five sites (table “Certification status of Lenzing operations – Chain of Custody”).
Site |
Country |
Main products |
FSC® CoC |
PEFC CoC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Lenzing |
Austria |
Viscose, modal, lyocell, dissolving pulp |
• |
• |
Paskov |
Czech Republic |
Dissolving pulp |
• |
• |
Purwakarta |
Indonesia |
Viscose |
• |
• |
Nanjing |
China |
Viscose, modal |
• |
• |
Heiligenkreuz |
Austria |
Lyocell |
• |
n. a. |
Grimsby |
United Kingdom |
Lyocell |
• |
n. a. |
Mobile |
USA |
Lyocell |
• |
• |
Prachinburi |
Thailand |
Lyocell |
• |
n. a. |
Indianópolis |
Brazil |
Dissolving pulp |
• |
n. a. |
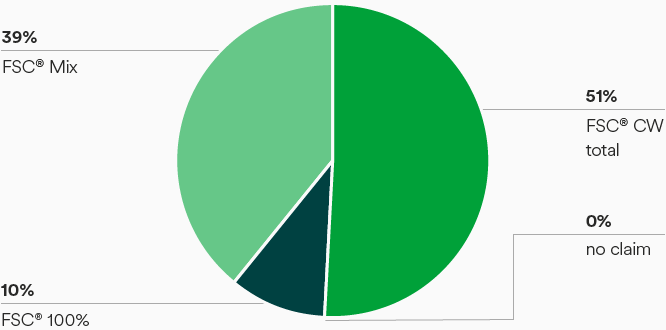
The PEFC certification is mainly used for wood sourced from Central Europe. FSC® certification of forests is not widespread in this region. Therefore, most of the wood sourced is procured with a PEFC certificate and receives FSC® Controlled Wood status at Lenzing sites after a due diligence process. All wood input to the Lenzing Group is either certified or controlled by the FSC® certification system (figure “Certification status - FSC® Mix and FSC® controlled wood”). The Lenzing site (Austria) has held the PEFC Chain of Custody certification as its main certificate for more than two decades. Since 2016, this has been complemented by a FSC® CoC (Chain of Custody) certificate.
Certification status
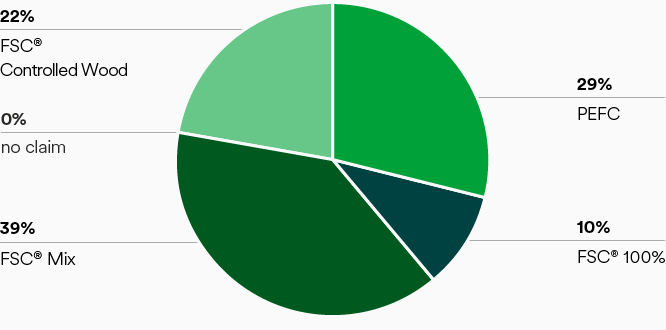
Basis: dissolving wood pulp by weight.
Certification status – overall certified and controlled wood
Certification status – FSC® Mix and FSC® controlled wood
Pulp suppliers can hold more than one forest-related certificate. Most of the pulp suppliers located in North America also carry certification from the Sustainable Forest Initiative (SFI), which is also a national member of and fully endorsed by the global PEFC certification scheme.
For detailed explanations of the certificates, controlled wood, and the internal due diligence system, please see the “Wood and pulp” focus paper.
Since forestry operations in Central Europe are generally small-scale, many small forest owners harvest wood for additional income and do not participate in a certification process. Therefore, Lenzing has to procure reliable but limited quantities of such wood that is not FSC® or PEFC certified from time to time. This category of wood is inspected in line with these standards. Strict forestry laws and enforcement in Central Europe also require all forest owners to pursue sustainable management. The Lenzing Wood and Pulp Policy and Supplier Code of Conduct are part of all wood purchasing activities and are presented to potential suppliers before the start of a business relationship. Deliveries can only be made to Lenzing if these conditions are accepted.
The Lenzing due diligence system for wood and pulp procurement includes regular formal audits. However, ongoing, day-to-day, informal, personal contact between Lenzing’s procurement team and suppliers is even more important. Supplier contracts can be terminated in response to severe sustainability findings. This has happened occasionally in the past when suppliers failed to remedy certain issues. In 2024, no such cases occurred.
1 Carle, J., and Holmgren, P. (2003). Working paper 79. Definitions Related to Planted Forests. In: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2003). Forest Resources Assessment Program Working paper series. Available at: <a href="https://www.fao.org/forestry-fao/25853-0d4f50dd8626f4bd6248009fc68f892fb.pdf">https://www.fao.org/forestry-fao/25853-0d4f50dd8626f4bd6248009fc68f892fb.pdf</a>
2Terms and Definitions, FRA 2020, FAO, 2018 (http://www.fao.org/3/I8661EN/i8661en.pdf).
3 Regional wood supply originates from the country where the pulp mill is situated and from neighboring countries from which wood can be transported directly without crossing a third country.
